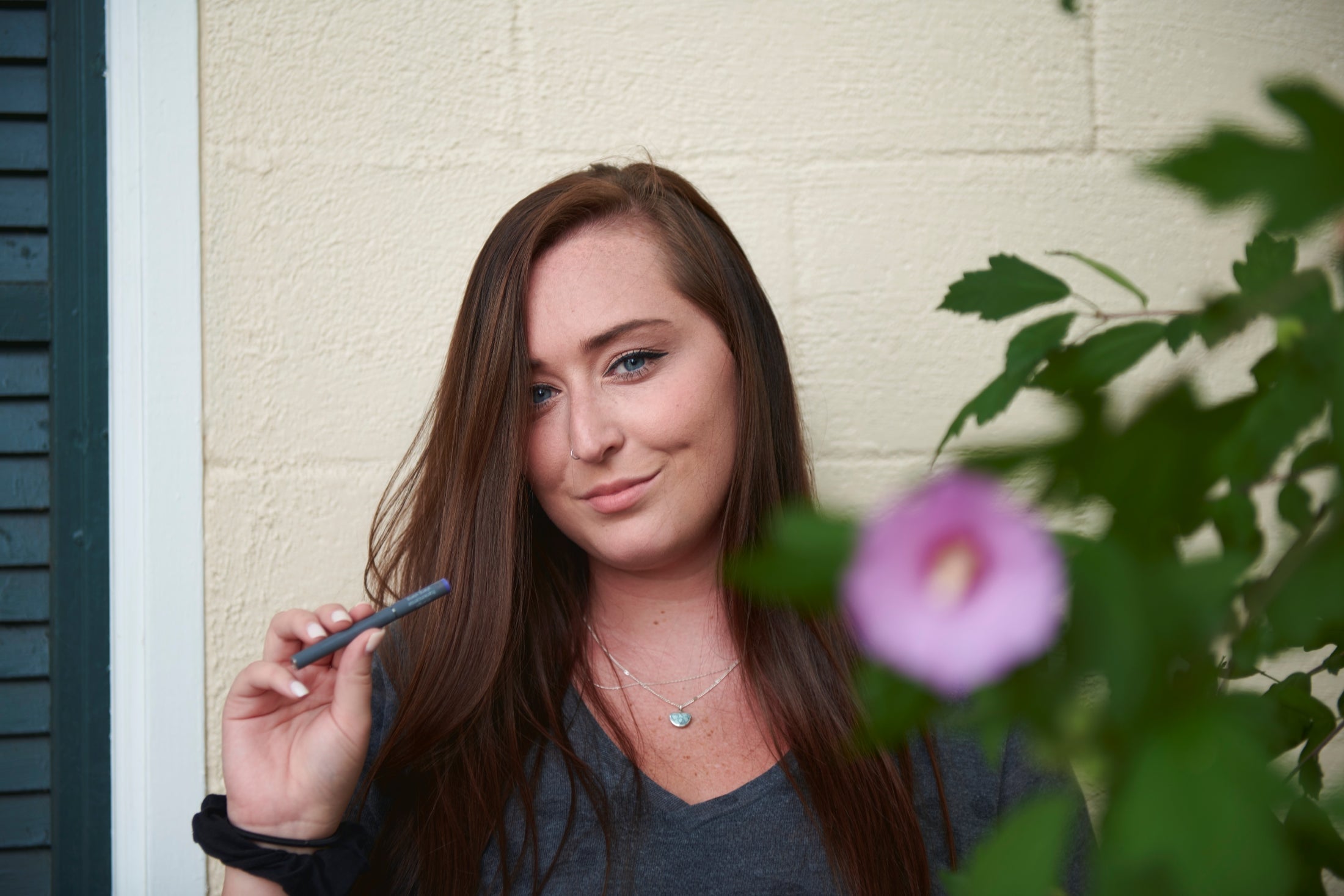
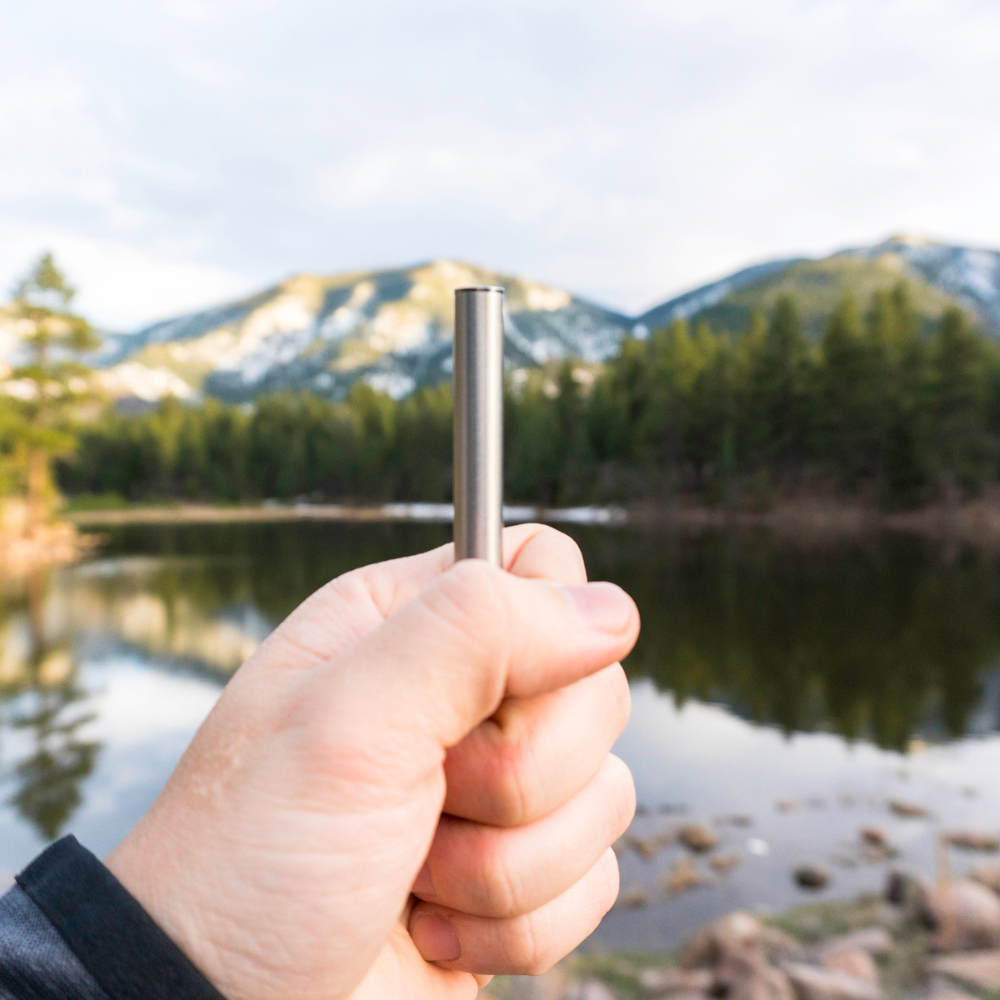
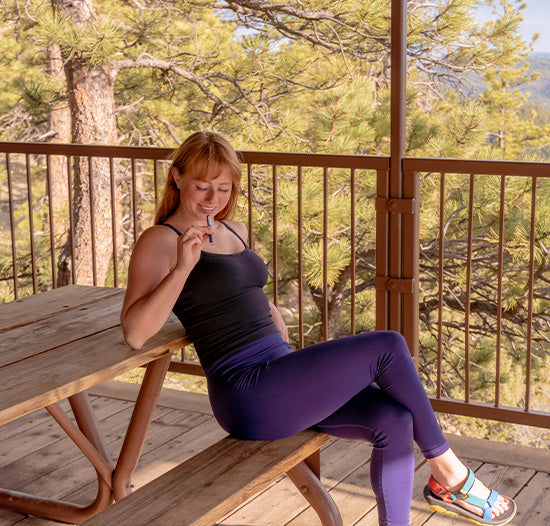
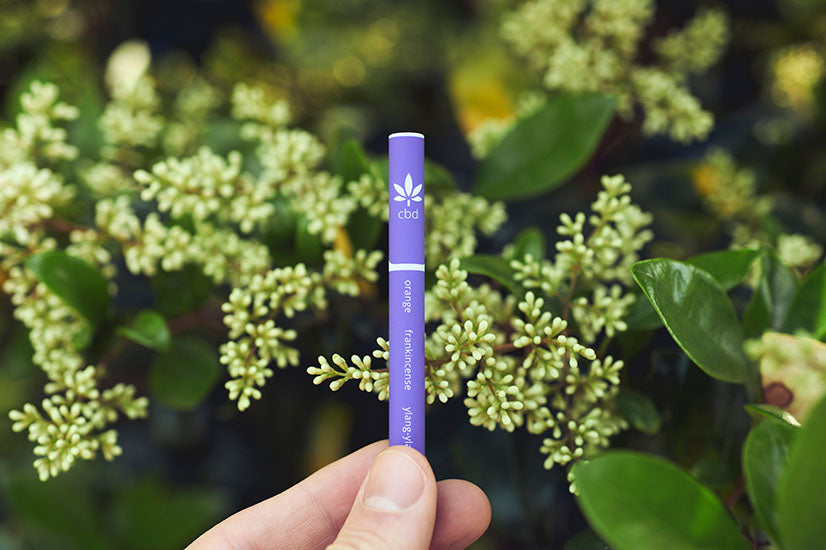
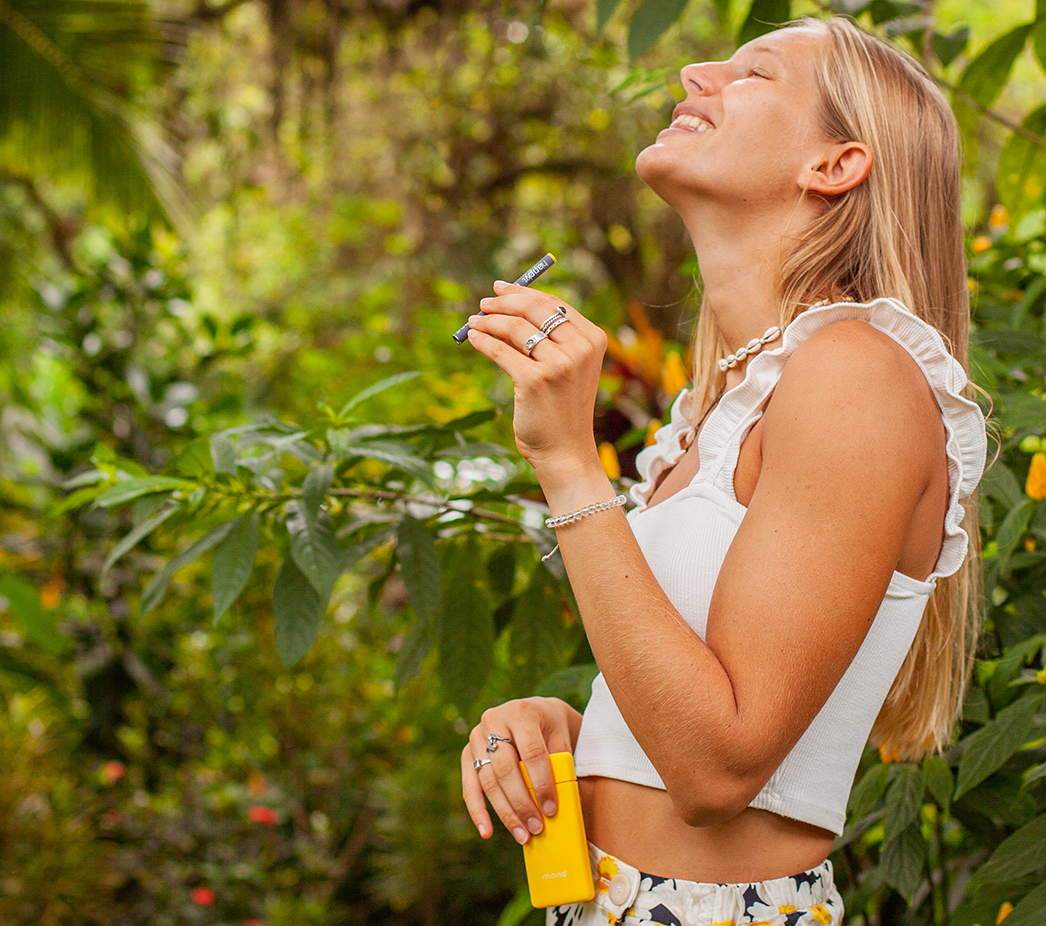
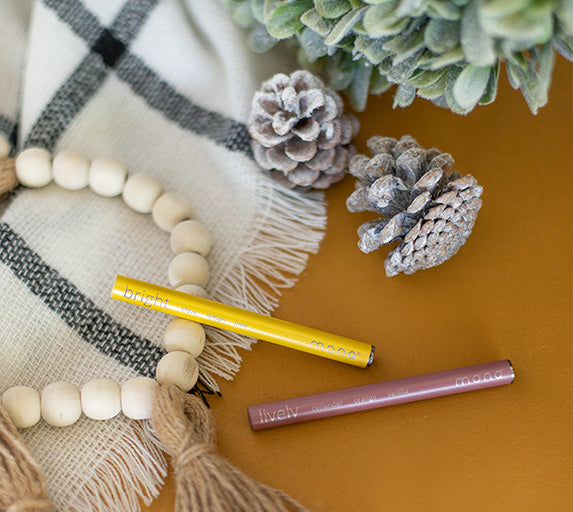
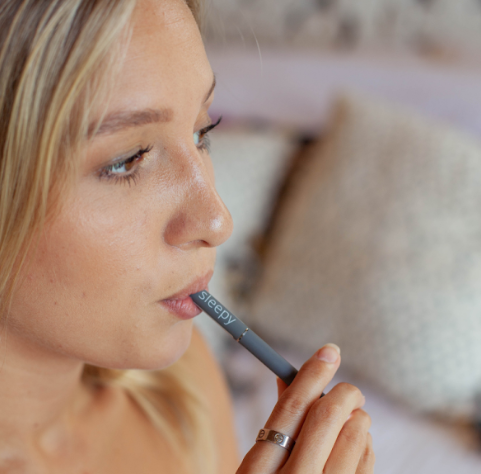
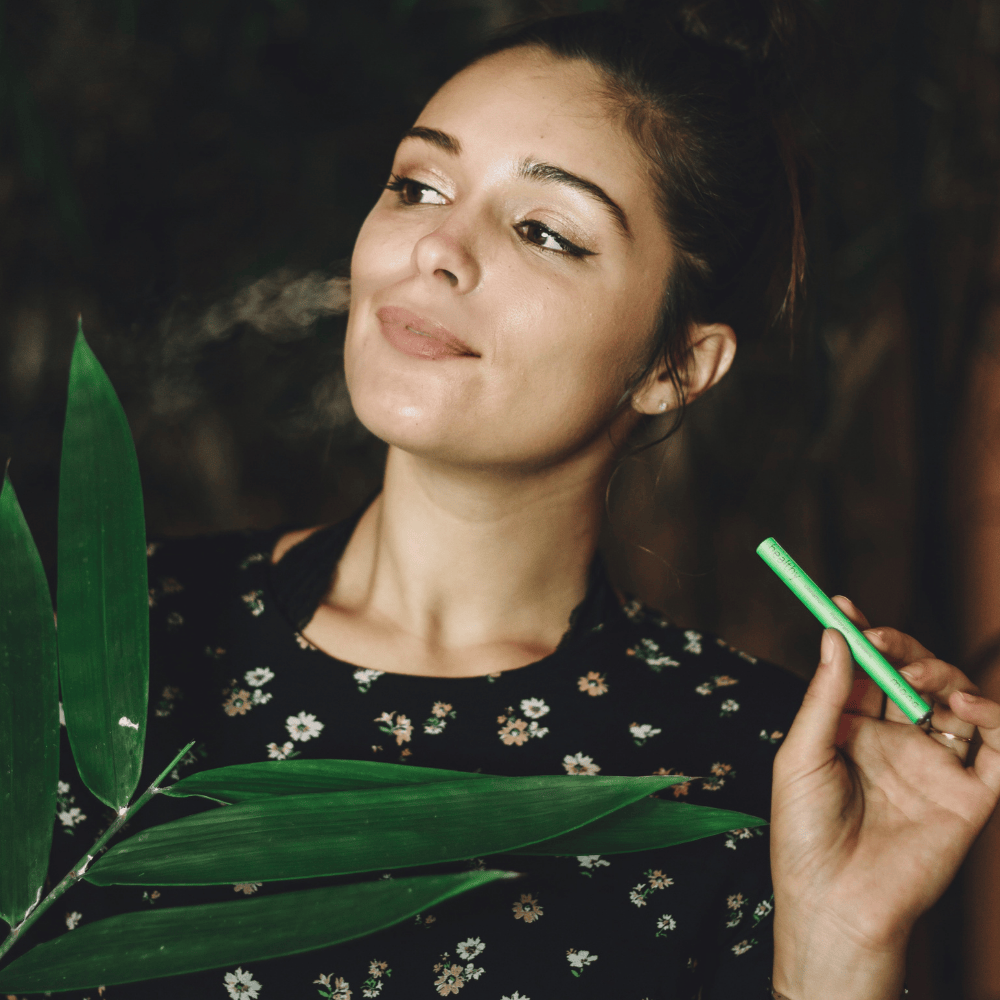
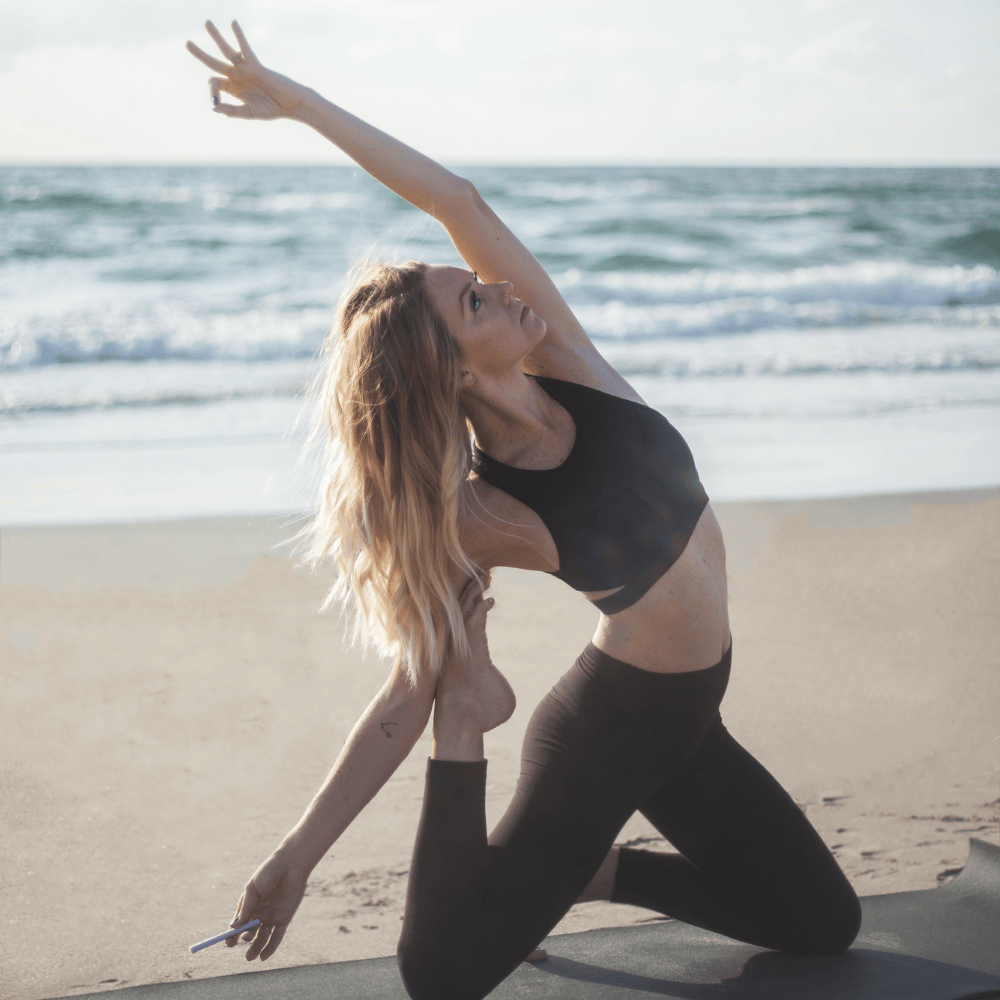
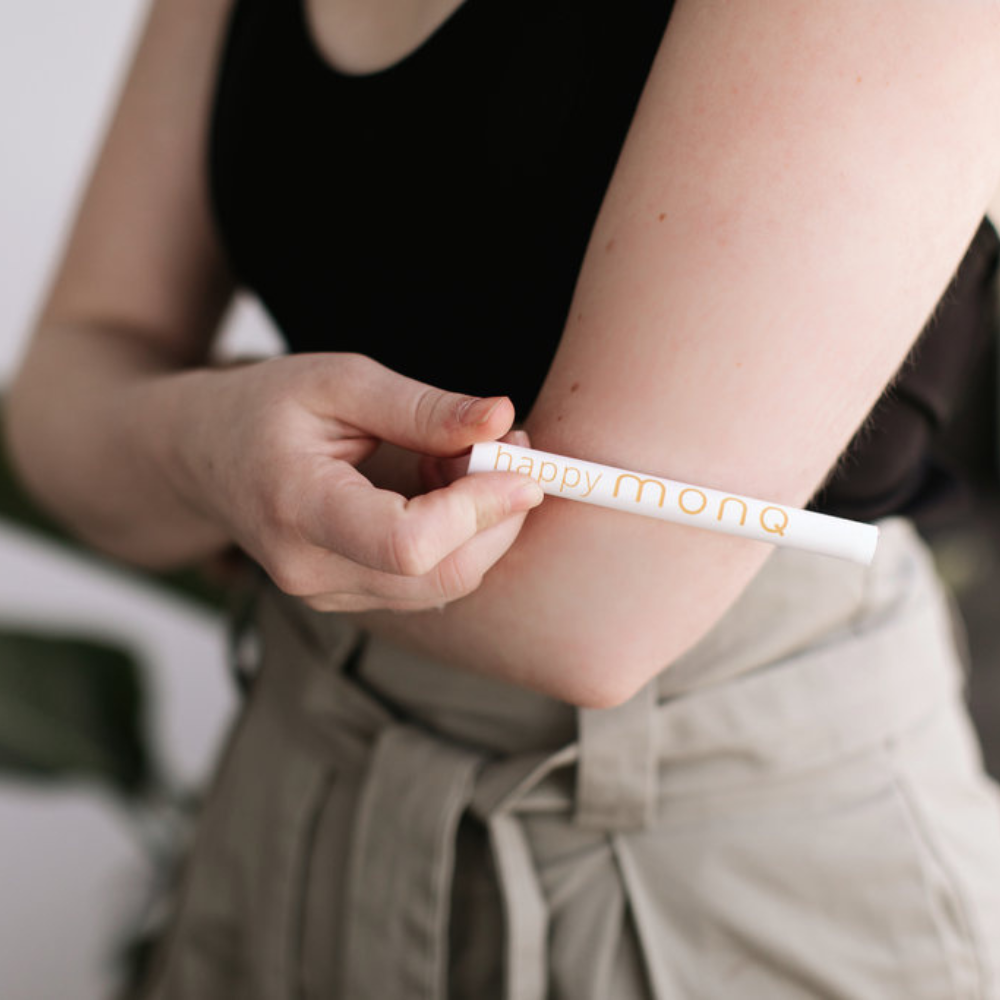
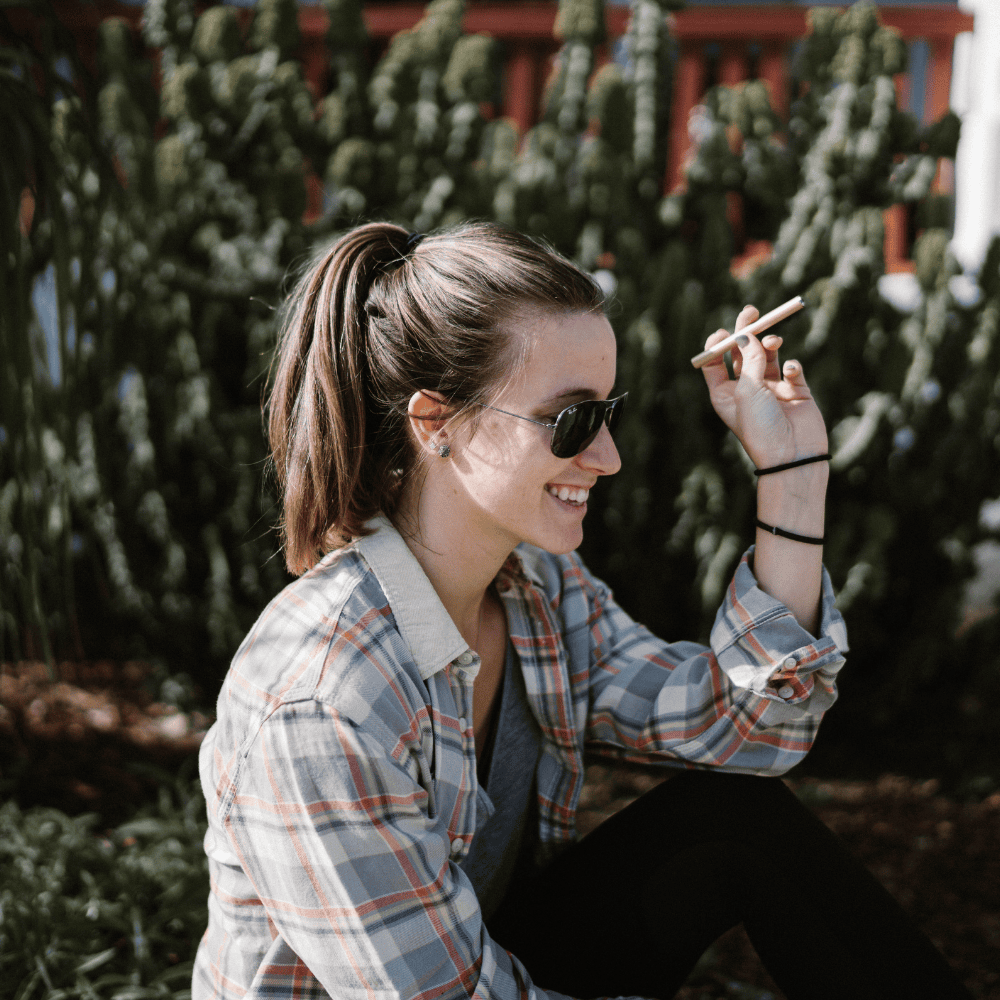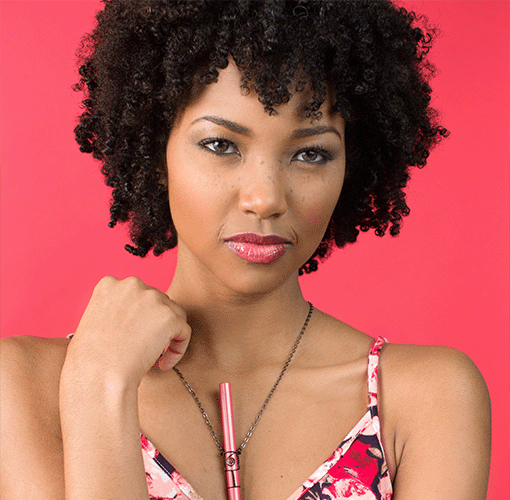Discover how personal aromatherapy diffusers make wellness simple, delivering calming, energizing, and inspiring scents wherever you go. With just a few mindful breaths, these beginner-friendly blends help balance your mood, boost focus, and promote relaxation.
Aromatherapy
CBD
Essential Oils & Diffusers
Forest Bathing - Forest Therapy
Hemp
Nicotine
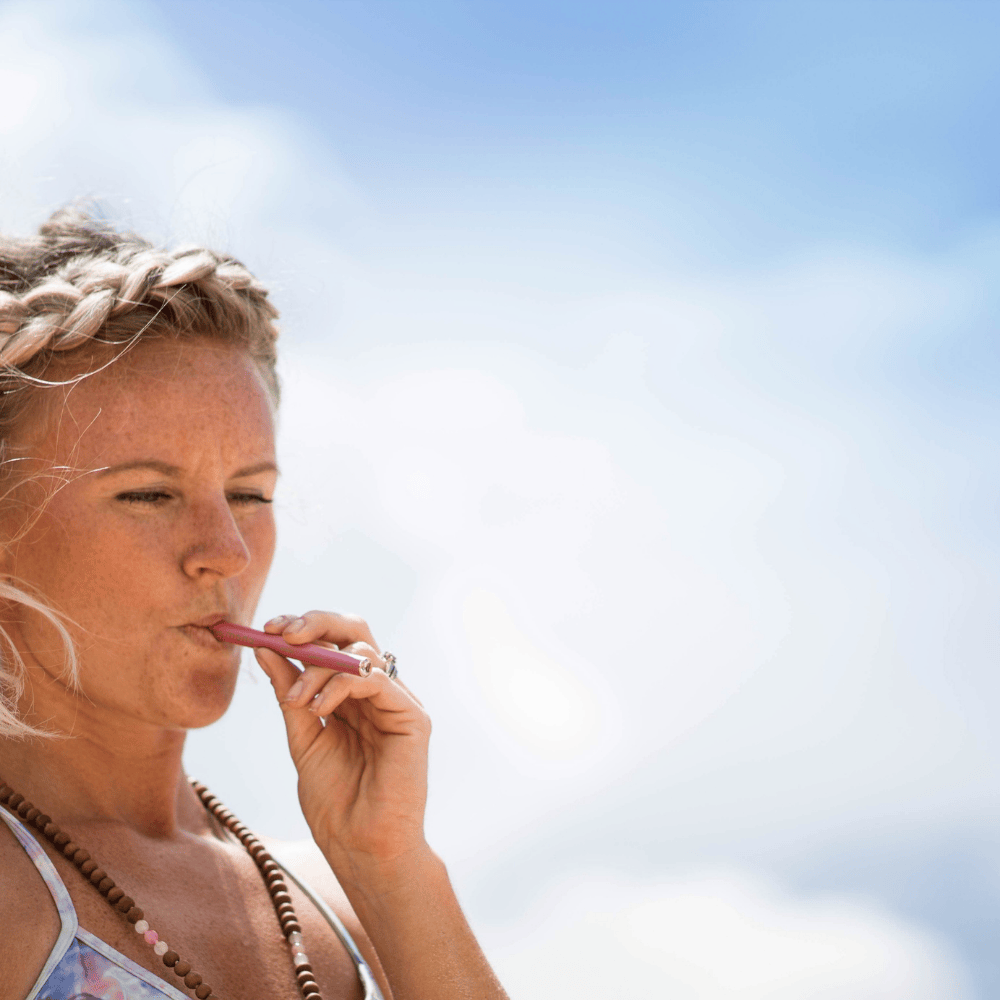
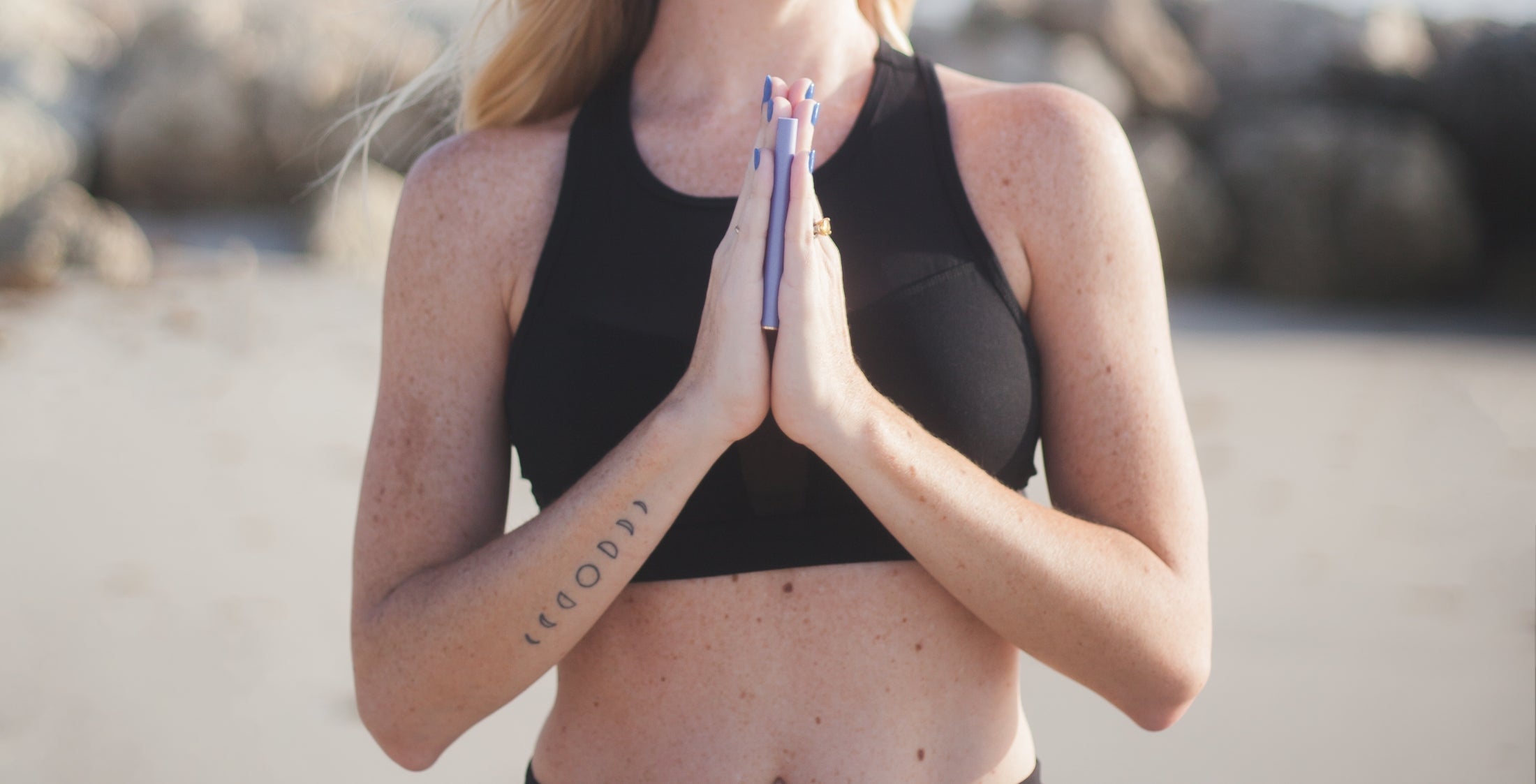
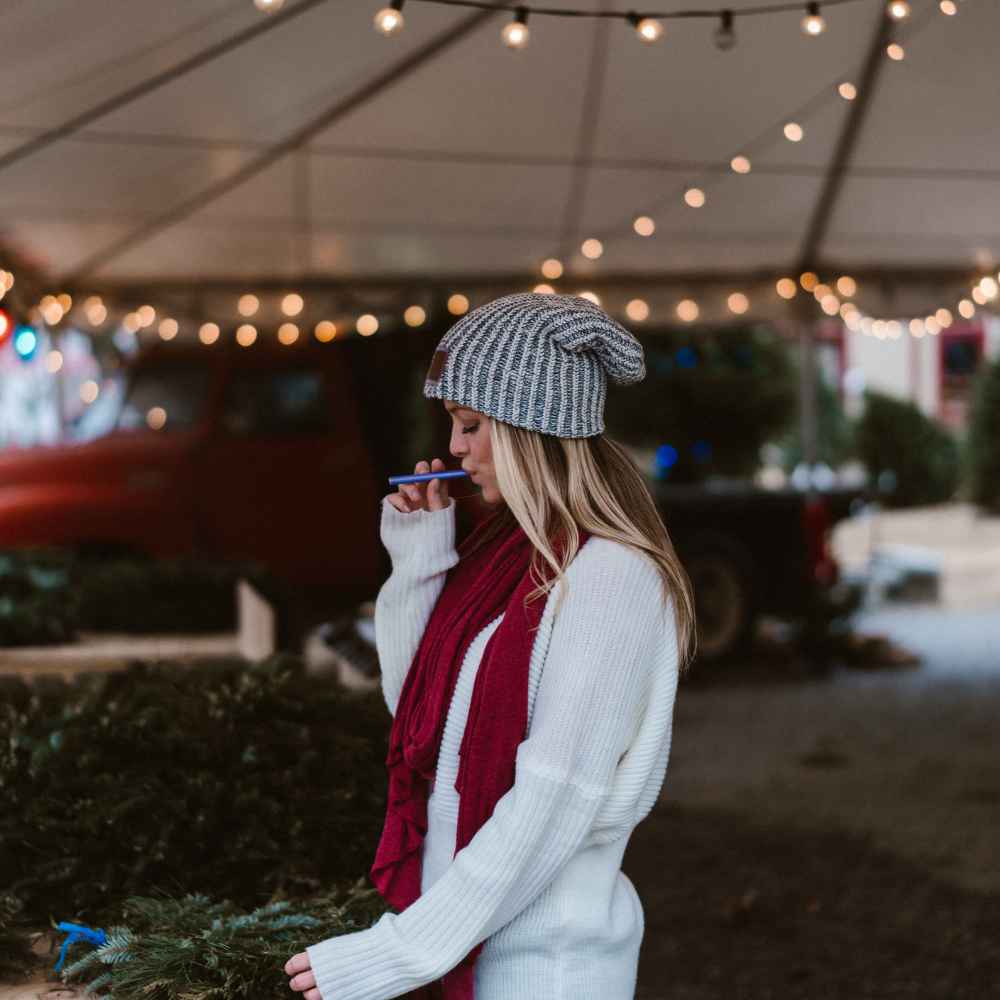
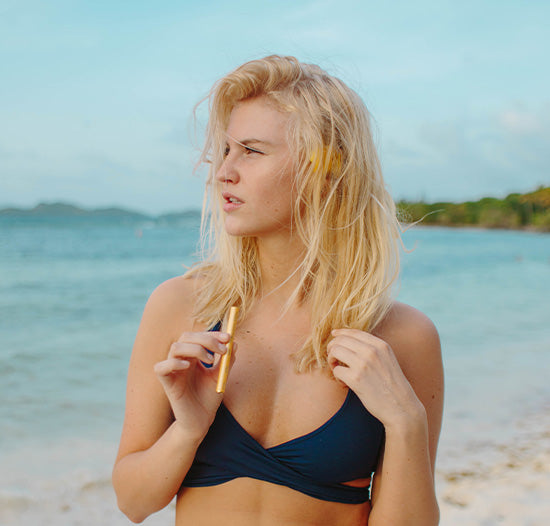
Experience calm anywhere with a nicotine-free personal aromatherapy diffuser, combining soothing plant-based aromas with mindful breathing for instant relaxation. MONQ makes stress relief simple, portable, and natural, turning a few intentional breaths into moments of peace throughout your day.
Beginner's guide to nicotine-free inhalation devices. Learn about wellness benefits, how to choose & where to buy. Start your wellness journey.
Nutrition
Sleep
Stress
Terpenes & Terpene Deficiency
Visual Aromatherapy Guide
Yoga, Meditation & Breathing
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.