MONQ is the pioneer of the personal aromatherapy industry—we created the first personal and portable aromatherapy diffuser. We are a small but mighty company based in Nashville, where we handcraft all of our pure essential oil blends.
By blending ancient aromatherapy practices with modern technology, we have revolutionized the way that customers experience the benefits of essential oils. Our organic blends are expertly crafted by our aromatherapist—from our flagship blend Zen (frankincense, ylang-ylang, and sweet orange), to our fan-favorite Relieve (ginger, spikenard, and helichrysum), to our top-selling Cozy blend (cardamom, cinnamon, and vanilla)—we are so proud to have over 40,000 5-star reviews from our customers who have enjoyed our products.
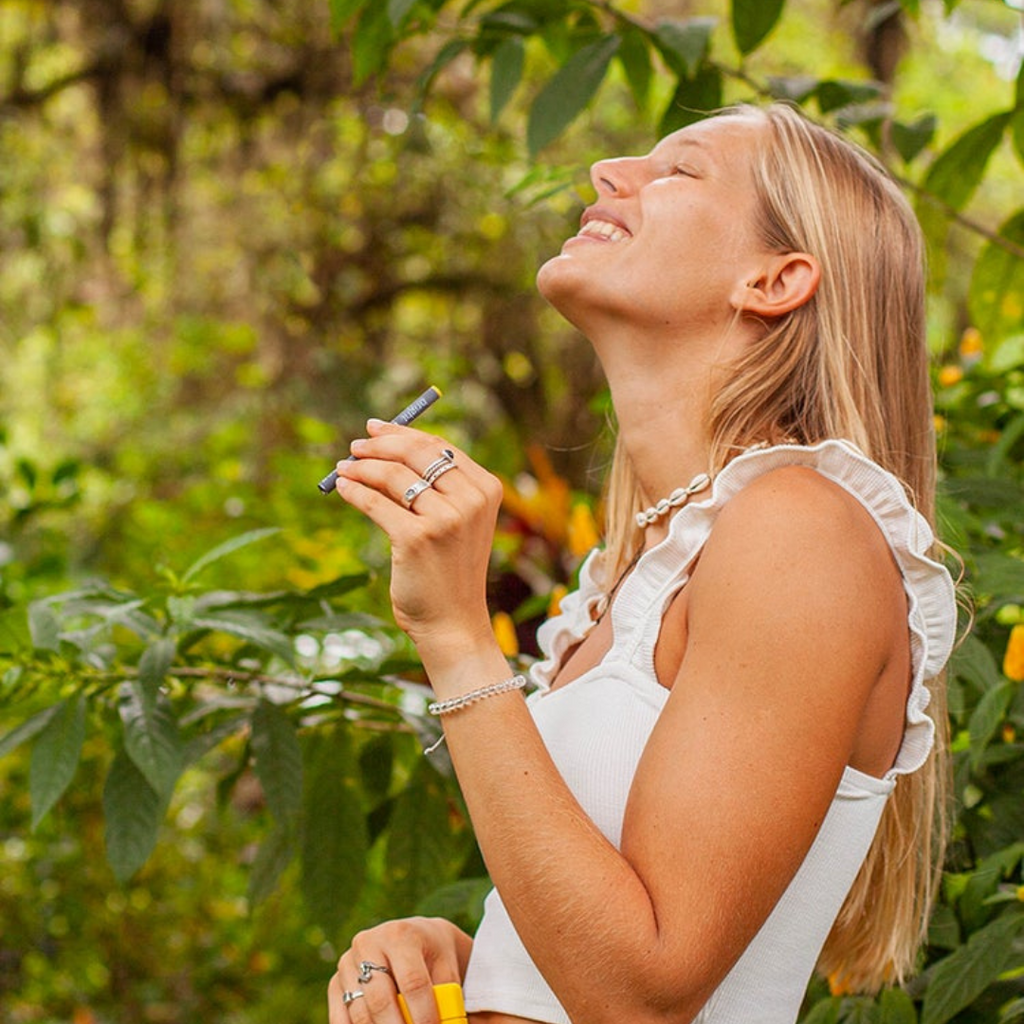
MONQ is designed to provide aromatherapy anywhere.
That said, we strongly encourage you to communicate directly with your phyisican or other healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Users with asthma or similar pulmonary conditions, and pregnant or nursing women, should not use MONQ. Some of our blends contain essential oils that the National Association for Holistic Aromatherapy recommends avoiding while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Remember, MONQ should not be inhaled into the lungs.
If you believe that you have had an adverse reaction, of any nature, to any of MONQ's products, please determine if you need urgent healthcare, and address your immediate health needs. Then contact us at your earliest convenience by any of the following methods:
- Call 844.936.6667
- Visit our Contact Us page
- Click the Support Button found on many pages
- Email us at Support@MONQ.com
For more information, visit monq.com/safety.
MONQ personal aromatherapy diffusers are not intended for persons under 18 years of age. We do not wish to encourage the hand-to-mouth habit that may lead to unhealthy habits, such as smoking.
All MONQ Aromatherapy Diffusers should be used with an AirTip. You gently squeeze the AirTip and the fragrance molecules exit from the hole at the tip of the device and experience the fragrance in the olfactory bulb.
We recommend using 2-3 brisk squeezes for each use, 2-3 uses in sequence, between 2-3 times per day. When using this method we estimate that each of your MONQ diffusers will last two months.
No.
MONQ Bottled Blends should not be used to refill your Original diffuser. These essential oils are not eJuice!
For aromatherapy on the go, try one of our Original diffusers or MONQ R—a sustainable, portable, and rechargeable aromatherapy diffuser that uses Blend PODs to help you can experience your favorite blends anywhere.
We’re so excited for you to try MONQ R! Each device includes a FlipCase, reusable diffuser battery, and 3 interchangeable Blend PODs. The PODs can be changed by twisting them onto or off the diffuser battery.
Approximately 200 uses from each POD. When you buy a MONQ R device—each with three Blend PODs—you get nearly 600 experiences of aromatherapy.
A fully charged diffuser battery will last approximately a week. Additionally, the FlipCase power pack is designed to keep the battery fully charged.
With Mix & Match, you choose your favorite color FlipCase and select any three Blend PODS.
To charge the diffuser, simply put it in the FlipCase, and the MONQ R case will charge the diffuser for you!
To charge the FlipCase, simply plug it into an electrical source using the provided USB charging cord. The light on the bottom of the MONQ R will light up when it is charging.
Yes. MONQ will guarantee the MONQ R device for six months after the purchase date. Please contact MONQ Happiness with questions about the device or guarantee.
Nearly all of our blends are available in Blend PODs, which are compatible with the MONQ R.
Original diffusers are not compatible with MONQ R.
No! We love our Original diffusers and know many of our customers do too! Original diffusers are perfect for trying out new blends. MONQ R is simply another, more sustainable option for our customers.
MONQ R was created to revolutionize the way you use aroatherapy—it’s rechargeable, reusable, responsible, and reinvented. There are lots of R’s in there, so MONQ R just seemed to fit!
Each MONQ R comes with 3 Blend PODs.
Want more? No problem! Blend PODs can be purchased individually!
Yes! The Blend PODS are recyclable.
You’re in luck! We have replacement Blend PODs that can be purchased on MONQ.com!
MONQ’s personal aromatherapy diffusers are filled with custom blends of essential oils, emulsified in coconut-derived vegetable glycerin. When gently heated, these blends leave the diffuser as aromatherapy-rich water vapor.
MONQ does not contain nicotine, artificial flavors or ingredients, tobacco, Vitamin E acetate, THC, or synthetic cannabinoids. Everything that goes into MONQ diffusers is organic and natural. This is by design.
MONQ devices are personal aromatherapy diffusers that gently heat essential oils and release aromatic water vapor to provide all the benefits of aromatherapy.
They are designed for adults looking to make a healthy lifestyle a habit.
There is no nicotine in MONQ. In fact, all MONQ blends are completely free of nicotine, tobacco, Vitamin E acetate, and artificial flavors and ingredients. MONQ diffusers have a variety of features and benefits.
Ingredients. MONQ’s devices are made with pure, organic essential oils in a carrier base of pure, organic vegetable glycerin.
Mechanism of action. The temperature of MONQ devices is intentionally kept as low as possible to preserve the beneficial properties of the essential oils. Further, MONQ works hard to minimize the amount of mist that is produced, rather than maximize it.
MONQ personal aromatherapy diffusers—a modern way to experience the ancient tradition of aromatherapy. You may consider it a Desktop Diffuser that you Hold In Your Hand!
MONQ personal aromatherapy diffusers work by gently heating essential oil blends creating a mist of aromatic compounds, water vapor, and carbon dioxide.
When using MONQ, air is breathed in through the mouth and exhaled through the nose.
This method of breathing MONQ allows the aromatherapy to waft past the olfactory bulb and ensures the user experiences the full benefits of the aromatherapy!
MONQ is not intended for inhaling into your lungs, as doing so merely lowers the effectiveness of the aromatherapy experience.
Some ask, “Do you smoke MONQ?”
MONQ products are portable aromatherapy diffusers, not smoking products. Our products do not contain nicotine or tobacco.
We create custom blends with essential oils sourced from reputable vendors throughout the United States. Each blend page discusses specific ingredients.
MONQ ingredients start as non-GMO, organically grown, and/or sustainably harvested, wildcrafted plants. Plants grown in the US are sourced from Oregon-Tilth Certified Organic processors when possible, and those grown internationally are verified organic by region-specific organizations. Plants are processed into essential oils and plant extracts at locations throughout the US, whenever available. The majority of oils are produced via steam distillation or CO2 extraction, without the use of alcohol.
Those oils are used to create MONQ’s proprietary essential oil blends, which are emulsified in a certified organic coconut-derived vegetable glycerin base.
MONQ blend labels feature three prominent ingredients that describe the flavor profile. However, the blends are formulated from as many as 20 unique oils.
A comprehensive list of our plant ingredients is available. Please note, if you are allergic to any essential oil, or any of our ingredients, contact MONQ or your healthcare provider, prior to using our product.
MONQ is dedicated to creating exceptional aromatherapy experiences. Below, we link to the most important features of our MONQ personal aromatherapy diffuser devices. No need to wonder what’s in your hand; it’s all here!
MONQ is for many people, and yet not for everyone!
MONQ diffusers are not intended for individuals under 18 or under the legal age in your location, individuals with respiratory illnesses or who are allergic to essential oils, or women who are pregnant or nursing. If this item is age-restricted in your state or country of residence, you must certify that you are of legal age to make this purchase.
MONQ does not want to encourage the familiar “hand to mouth” habit in impressionable minors.
MONQ should not be used by those with respiratory illnesses or chronic pulmonary conditions, such as asthma or COPD.
Because some MONQ products contain essential oils that the National Association for Holistic Aromatherapy recommends to avoid during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, MONQ is not recommended for use by those women. To read the entire article, please visit NAHA.
See our disclaimer for more detailed exceptions and explanations.
No! MONQ does not contain any illegal or addictive substances. Furthermore, MONQ does not contain nicotine, artificial ingredients or flavors, tobacco, Vitamin E acetate, THC, or synthetic cannabinoids.
Our lab tests have found MONQ to be free of formaldehyde, acrolein, nickel, tin, lead, and aluminum.
MONQ is legal in US states and in the overwhelming majority of countries around the world. Please see our shipping policies for some exceptions.
MONQ is 100% pure organic and natural.

MONQ diffusers are the most natural and convenient way to experience aromatherapy.
Feel the Way You Want® and experience all the benefits of pure Therapeutic Air®
in one simple breath, anytime, anywhere.

Use Gently
When you use MONQ gently, aromatherapeutic molecules pass the olfactory nerve endings in your upper nasal passageway. This action is the first step to noticeable effects.
While the aromatherapy effect from the olfactory nerves frequently starts immediately, it usually does not peak for at least a few minutes. We recommend that you gently and intermittently, as opposed to using it continuously. MONQ should be used with the AirTip.
Learn About The Airtip
you choose how long it lasts you
Use as much or as littLe as you want
MONQ’s blends are robust, so most users are encouraged to be more gentle in using it than they might have initially anticipated (about 2-3 experiences every few hours, up to 9 per day).
Only one or two essential oils are used in most aromatherapy blends. MONQ is different because we formulate and supply more complex blends, which leads to a synergistic effect that allows for aromatherapy through a relatively dilute base of essential oils.
We encourage gentle, moderate use of MONQ diffusers. Remember, MONQ should not be inhaled into the lungs, and doing so merely dilutes the beneficial effects of the terpenes you are breathing.

The above information relates to studies of specific individual essential oil ingredients, some of which are used in the essential oil blends for various MONQ diffusers. Please note, however, that while individual ingredients may have been shown to exhibit certain independent effects when used alone, the specific blends of ingredients contained in MONQ diffusers have not been tested. No specific claims are being made that use of any MONQ diffusers will lead to any of the effects discussed above. Additionally, please note that MONQ diffusers have not been reviewed or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. MONQ diffusers are not intended to be used in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, prevention, or treatment of any disease or medical condition. If you have a health condition or concern, please consult a physician or your alternative health care provider prior to using MONQ diffusers. MONQ blends should not be inhaled into the lungs. Why? It works better that way.